Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology. Cellular respiration stores chemical energy in the form of phosphorylated nucleotides (primarily atp) by means of oxidative reactions and makes it available to other reactions. Cellular respiration also releases the energy needed to maintain body temperature despite ongoing energy transfer to the surrounding environment.
Cellular respiration is a process that uses oxygen, nitrate, or sulfate to break down nutrients to generate a cell's energy. Secondly, respiration may refer to internal respiration, which involves a gas exchange between the blood and body cells. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate (atp).
This Means That More Energy Is Being Used By The Molecules At Room Temperature So They Would Have To Go Through Cellular Respiration More To Gain Enough Energy To Balance Out The Energy Lost.
The word glycolysis literally means “glucose splitting,” which is exactly what happens in this stage. The respiration can be aerobic, which uses glucose and oxygen, or anaerobic which uses only. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells in plants and animals break down sugar and turn it.
Students Can Work In Pairs Or Small Groups To Accommodate Different Class Sizes.
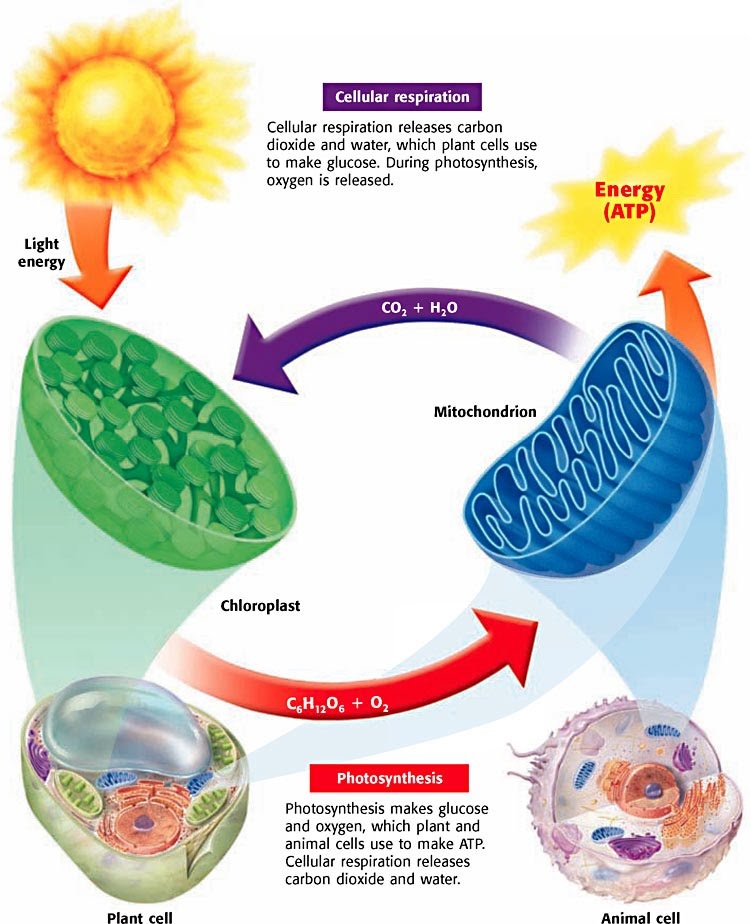
If you are searching for information on the formula of cellular respiration equation, the following biologywise article will prove to be useful. Don't confuse respiration with photosynthesis. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form.
I Think 5 Stars Are Less For Your Work.
C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6 o 2 → 6 h 2 o + 6co 2 + energy. Cellular respiration is the set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (), and then release waste products. Likewise, “biological machines” also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.perhaps the second most important molecule (dna is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as atp).basically, atp serves as the main energy.
Cellular Respiration Is A Biological Process Used By Most Organisms, Enabling Them To Produce Atp In Large Amounts, Which Can Be Used To Provide Energy For Cells (Campbell, 2008).
Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells convert sugar, amino acids and fatty acids into energy utilized by the cell. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulate cellular signaling and dictate biological outcomes,. C6h12o6 + o2 → h2o + co2.all organisms, including those capable of photosynthesis, go through the process of cellular respiration.
Aerobic Respiration Requires Oxygen To Fully Oxidise The Organic Molecule.
C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6o 2 → 6co 2 + 6h 2 o + chemical energy (in atp). Secondly, respiration may refer to internal respiration, which involves a gas exchange between the blood and body cells. Objectives from the ap biology curriculum framework, as indicated below