Cellular Respiration Process Equation. Along the way, some atp is produced directly in. Cellular respiration can be defined as a series of metabolic reactions that typically occur in cells so as to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (atp).
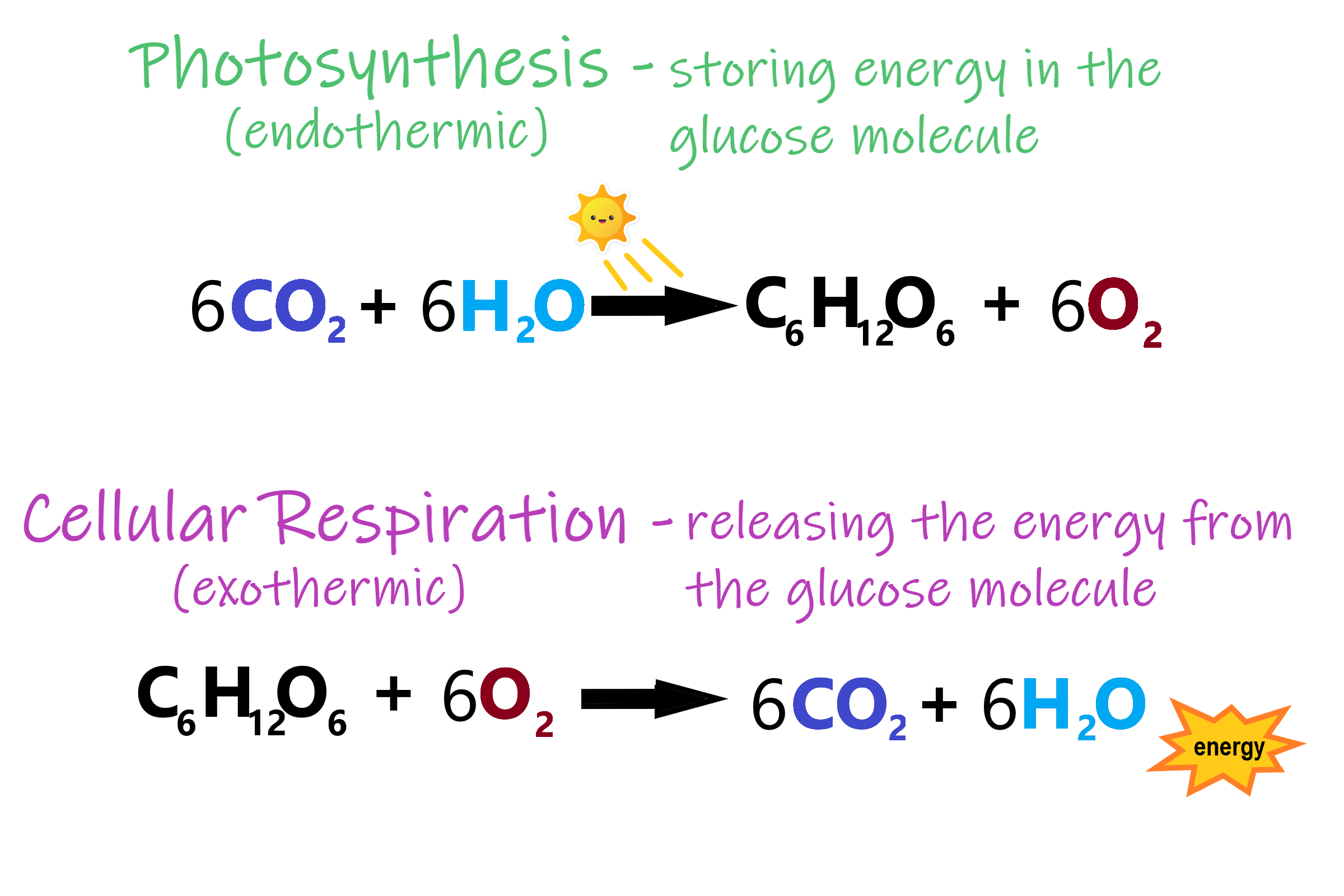
Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is c6h1206 + 6o2 = 6co2 + 6h2o + energy (atp). The reduction of oxygen to water with the passage of electron to oxygen is the reduction reaction.
It Is A Biochemical Pathway That Releases Energy From The Chemical Bonds In Glucose, And In Turn, This Energy Is Used To Carry Out The Other Essential Functions Of Life.
Breathing or ventilation is the process whereby a multicellular organism gets oxygen into its body. Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. Glucose sugar oxygen carbon dioxide water energy as atp chemical equation.
Cellular Respiration Helps Cells Break Sugar Which Further Helps In Producing Energy.
In order to do this, the cells use that oxygen that you breathe in. This oxygen is then transported to the cells by various means (in most vertebrates it is carried from The process of anaerobic cellular respiration is different in plants and animals.
When You Do This, You Are Taking In Oxygen And Releasing Carbon Dioxide, Two Important Gasses Involved In Cellular Respiration.
The overall (unbalanced) chemical equation for cellular respiration is: The lactic acid then needs to be oxidised later to carbon dioxide and water afterwards to prevent it building up. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as:
In This Process, Both Plants And Animals Break Down Simple Sugars Into Carbon Dioxide And Water And Release Energy In The Form Of Adenosine Triphosphate (Atp).
Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as: Waste products include carbon dioxide and water. Human cellular respiration is an example.
The Equation For Aerobic Respiration Shows Glucose Being Combined With Oxygen And Adp To Produce Carbon Dioxide, Water, And Atp:
Each and every living cell follows cellular respiration. Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create atp, a chemical which the cell uses for energy. Basically, photosynthesis is a chemical process through which light energy is used to convert/assemble inorganic material (water and carbon dioxide) into organic molecules.