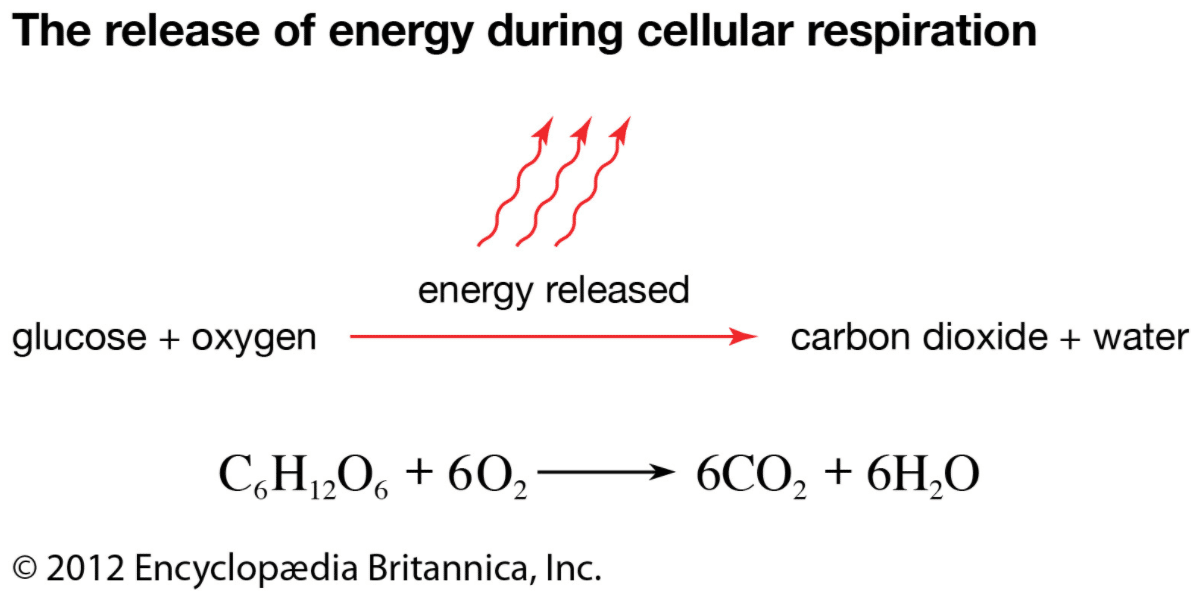
Cellular Respiration Formula Equation. Take a deep breath, then release the air out. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as:
Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. 6co2 + 6h2o → c6h12o6+ 6o. C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6 o 2 → 6 co 2 + 6 h 2 o + 38atp ( glucose +.
H2O, Nad+, Fad+ • Aerobic/Anaerobic
Cellular respiration (aerobic) c6h12o6 + 6o2 → 6co2 + 6h2o + 32 atp about this quiz & worksheet. Electron transport is the most complex and productive pathway of cellular respiration. Does glycolysis produce 2 or 4 atp?
C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 → 6 Co 2 + 6 H 2 O + 38Atp ( Glucose +.
The chemical formula for cellular respiration is. When you do this, you are taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide, two important gasses involved in cellular respiration. C 6 h 12 o 6 (glucose)+ 6o 2 + 36 adp (depleted atp) + 36 p i (phosphate groups)→ 6co 2 + 6h 2 o + 36 atp
Name The Reactants Of Cellular Respiration As Shown By The Chemical Equation:
There isn't a simple equation for that process, it is a very complex cycle called oxidative phosphorylation. Here, you will learn the definition, location, processes, and formula for cellular. The word equation for cellular respiration is glucose (sugar) + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + energy (as atp).
Cellular Respiration Is Defined As The Conversion Of Fuel Into Energy And Nutrients Within The Mitochondria And Cytosol Of Cells.
The chemical equation for aerobic respiration is glucose + oxygen gives carbon dioxide + water + energy whereas the equation for anaerobic respiration is glucose, giving lactic acid + energy. Notice that the equation for cellular respiration is the direct opposite of photosynthesis: #c_6h_12o_6 + o_2 → co_2 + h_2o + energy#
Cellular Respiration Is The Reverse.
This process breaks down glucose into six carbon dioxide molecules and twelve water molecules. However, cellular or aerobic respiration takes place in stages, including glycolysis and the kreb's cycle. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as: